Telescopium telescopium Shells Waste As Fe (II) Adsorbent
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46252/jsai-fpik-unipa.2019.Vol.3.No.2.88Keywords:
Adsorption, Iron (Fe2 ), Temberungun Shells (Telescopium telescopium)Abstract
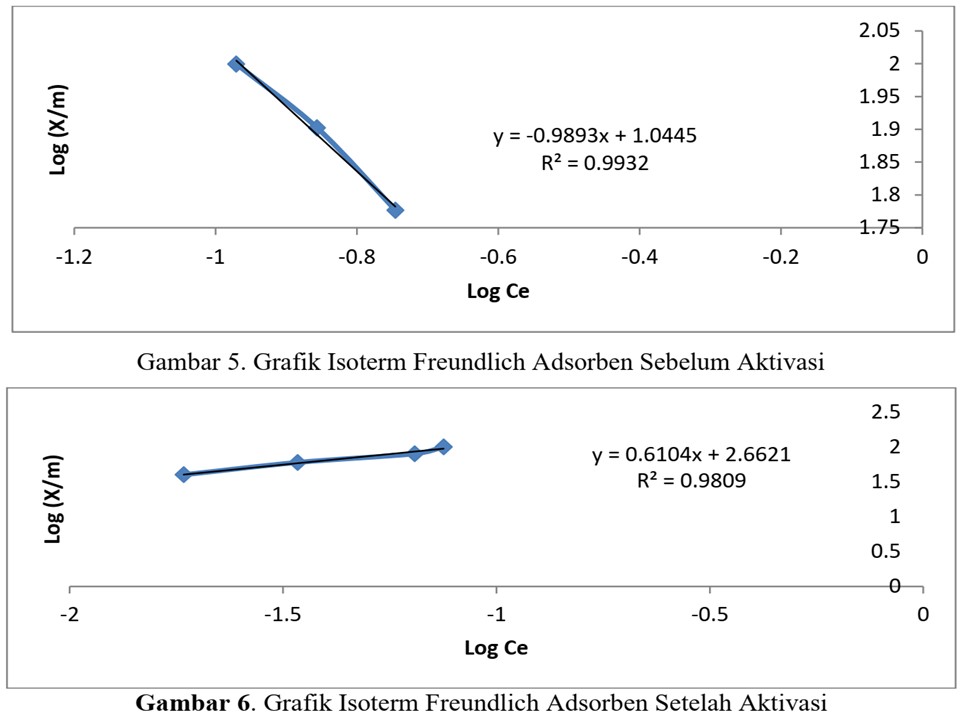
The decrease in water quality is caused by the presence of pollutants in the form of organic and inorganic components. Inorganic components, including heavy metals, one of which is iron (Fe). Adsorption is one of the technologies that can be used to absorb heavy metals where the adsorbent used in this study is a shell of a shell (Telescopium telescopium) to absorb iron (Fe2+). This research aims to utilize the waste of the mussel shells (Telescopium telescopium) as an adsorbent for heavy metal iron (Fe2+). The study was divided into three stages, namely the adsorbent surface characterization, determining the optimum time and determining the adsorption capacity. All stages of the study were carried out on adsorbents that were not activated and NaOH. The results showed the largest pore size after activation was 1,398 µm, while the adsorbent before activation, the largest pore size was 844.8 nm. The surface acidity of the adsorbent before activation is 5.28 mmol / g and after activation has a value of 6.74 mmol / g. The optimum time of absorption of ferrous metal ions (Fe2+) before and after activation is 60 and 30 minutes. The adsorption capacity of the adsorbents before and after activation was 11,07899 mg / g and 459,3038 mg / g, respectively. It was concluded that the shell of a temberungun shell (Telescopium telescopium) can be used as an adsorbent for heavy metal ions (Fe2+)
Downloads
References
Hsu T.-C. (2009) Experimental as-sessment of adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution by oyster shell pow-der. Journal of Hazardous Materials 171, 995–1000.
Hutapea T. P. H., Yusuf B. and Purba R. (2016) Pemanfaatan Batu Padas Dalam Mengadsorpsi Logam Berat Pb (II) di Perairan. . Oktober., 4.
Jeon D. and Yeom S. (2009) Recycling wasted biomaterial, crab shells, as an adsorbent for the remov-al of high concentration of phosphate. Bioresource tech-nology 100, 2646–9.
Khan A. A. Efektivitas pemanfaatan limbah cangkang kerang dara (anadara granosa) sebagai media adsorben logam cu (ii) da-lam air. , 10.
Kusumaningrum W. (2016) penggunaan karbon aktif dari ampas tebu sebagai media ad-sorbsi untuk menurunkan ka-dar Fe (besi) dan Mn (mangan) pada air sumur gali di desa gelam candi. 14, 7.
Lestari S. The Influence of Wight and Contact time to adsorb lead (II) by Adsorbent. , 4.
Low K. S., Lee C. K. and Wong S. L. (1995) Effect of Dye Modifi-cation on the Sorption of Cop-per by Coconut Husk. Envi-ronmental Technology 16, 877–883.
Meisrilestari Y., Khomaini R. and Wijayanti H. (2013) Pembuatan Arang Aktif Dari Cangkang Kelapa Sawit Dengan Aktivasi Secara Fisika, Kimia Dan Fisika-Kimia. 2, 7.
Nurdila F. A. and Asri N. S. (2015) Adsorpsi Logam Tembaga (Cu), Besi (Fe), dan Nikel (Ni) dalam Limbah Cair Buatan Menggunakan Nanopartikel Cobalt Ferrite (CoFe2O4). , 5.
Siaka I. M. (2008) Korelasi Antara Kedalaman Sedimen Di Pelabuhan Benoa Dan Konsen-trasi Logam Berat Pb dan Cu. JURNAL KIMIA, 10.
Syauqiah I., Amalia M. and Kartini H. A. Analisis Variasi Waktu Dan Kecepatan Pengaduk Pada Proses Adsorpsi Limbah Logam Berat Dengan Arang Aktif. , 10.
Tangio J. S. Adsorpsi Logam Timbal (Pb) Dengan Menggunakan Bi-omassa Enceng Gondok (Eich-horniacrassipes). , 7.
Wu Q., Chen J., Clark M. and Yu Y. (2014) Adsorption of copper to different biogenic oyster shell structures. Applied Surface Science 311, 264–272.