Potential of Celery (Apium graveolens) Ethanol Extract for Masculinization of Betta Fish (Betta sp)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46252/jsai-fpik-unipa.2019.Vol.3.No.2.87Keywords:
Betta fish; Celery Ethanol Extract; Immersion; Masculinization; Reversal SexAbstract
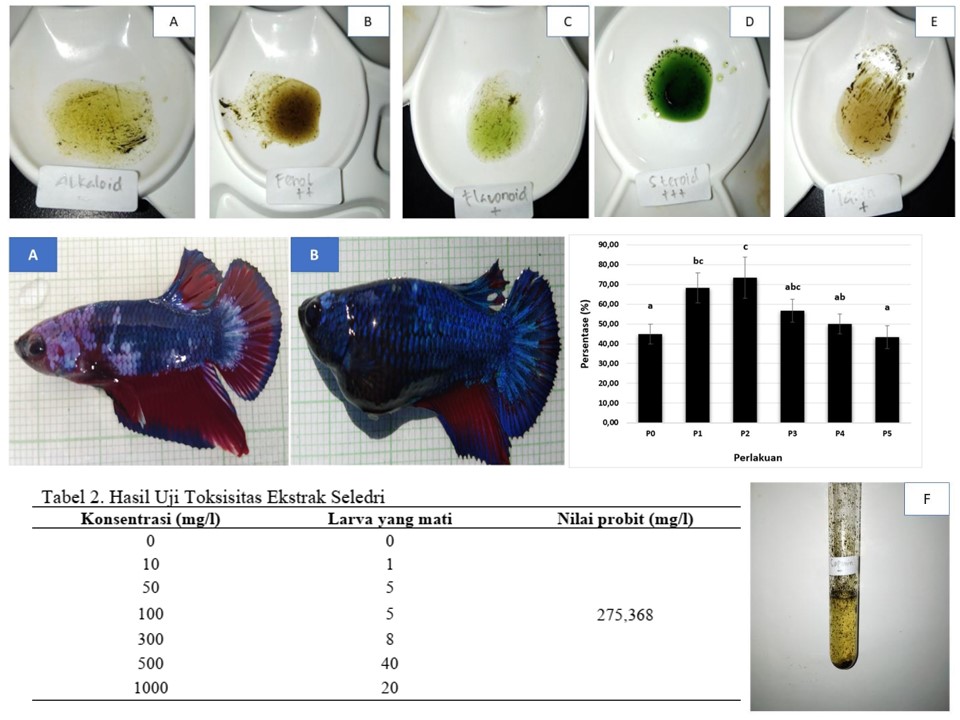
Betta fish is one of the excellent ornamental fish because it has high economic value. Betta fish that have economic value are male betta fish because it has a beautiful shape. To increase male fish production, steps can be done by masculinization. This study aims to determine the effect of celery extract on the percentage of male betta fish by masculinization. This study uses a completely randomized design (CRD) with 6 treatments and 3 replications. The treatment in this study was 7-day-old betta fish larvae soaked in celery extract media with different concentrations for 8 hours. The treatment is the addition of celery extract as much as 5 mg / L (P1), 10 mg / L (P2), 20 mg / L (P3), 40 mg / L (P4), 80 mg / L (P5) and without the addition of celery extract as a control (P0). Based on phytochemical testing, celery ethanol extract contains steroids, flavonoids, tannins, and phenols. The results showed that the addition of celery extract with different concentrations had a significant effect on the percentage of male betta fish, but there was no significant effect on survival rates.
Downloads
References
Atmadjaja J dan Sitanggang M. (2008). Panduan Lengkap Budidaya dan Perawatan Cupang Hias. Jakarta : Agromedia .
Awaludin, dan Ridwan A. (2016). Peningkatan Survival Rate Benih Udang Windu (Peaneus Monodon) Dengan Perendaman Ekstrak Etanol Karamunting (Melastoma Malabahricum). Jurnal Harpodon Borneo, 9(1): 32-35.
Awaludin, Yulma dan Kartina. 2019. Identification of Secondary Metabolites from Ethanol Extract of Ciplukan (Physalis angulate) Leaves and Toxicity Test on Post-Larvae of Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Jurnal Ilmiah Perikanan dan Kelautan, 11(2):92–99.
Carballo J L, Inda Z H, Perez P dan Gravalos M D G. 2002. A Comparison Between two Brine Shrimp Assays to Detect in Vitro Cytotoxicity in Marine Natural Products. BMC Biotechnology. 2:17.
Ferdian A, Muslim dan Fitrani, M. 2017. Maskulinisasi Ikan Cupang (Betta sp.) Menggunakan Ekstrak Akar Ginseng (Panax Sp.). Jurnal Akuakultur Rawa Indonesia, 5(1) :1-12 (2017).
Harbone J. B. 1996. Metode fitokimia penuntun cara modern menganalisis tumbuhan. Bandung: Penerbit ITB.
Homklin S, Watanodorn T, Ong S K dan Limpiyakorn T. 2009. Biodegradation of 17alphamethyltestosterone and isolation of MTdegrading bacterium from sediment of Nile tilapia masculinization pond. Water Science and Technology 59: 261–265.
Kementerian Kelautan dan Perikanan. 2019. Laporan Indikator Kinerja Triwulan I-2019. Direktorat Jenderal Perikanan Budidaya.
Martha R D dan Zummah, A. 2018. Phytochemical Testing And Determination Of Kinetic Parameters Enzyme With Water Infusion Of Celery Extracts. Jurnal Wiyata. Vol. 5 No. 2.
Meyer B. N, Ferrigni N. R, Putnam J E, Jacobsen L B, Nichols D E, dan Mc Laughlin J L. (1982). Brine Shrimp: A Convenientgeneral bioassay for Active Plant Constituents, Planta Medica, 45: 31-34.
Ostrow M E. 1989. Betta's.T. F..H Pub. Inc. Canada. h.91.
Piferrer F. dan W. Donaldson. 1989. Gonadal differentiation in coho salmon, oncorhynchus kisutch after a single treatment with androgen at Different stages during ontogenis. J. Aquaculture. 234:229-239.
Priyono E, Muslim dan Yulisman. 2013. Masculinitation of guppy (Poecilia reticulata) by dipping pregnant guppy in honey solution with different dipping time. Jurnal Akuakultur Rawa Indonesia. 1(1): 14-22.
Putra D A. 2011. Maskulinisasi Ikan Guppy (Poecilia reticulata) Melalui Perendaman Induk dalam Berbagai Aras Dosis Propolis. Lampung. Skripsi. Universitas Lampung.
Samejo M Q, Memon S, Bhanger MI dan Khan K M. 2013. Isolation and characterization of steroids from Calligonum polygonoides., J. Pharmacy Res., 6, 346-349.
Soelistyowati D T, Martatih E. dan Arfah H. 2007. Efektifitas penggunaan madu terhadap pengarahan kelamin ikan gapi (Poecilia reticulata). J. Akuakultur Indonesia. 6(2):155-160.
Sugandy dan Irawan. 2001. Budidaya Ikan Cupang Hias. Penerbit Agro Media Pustaka, Jakarta, hal 21-22.
Sumantadinata K dan Carman O. 1995. Teknologi Ginogenesis dan Seks Reversal dalam Pemuliaan Ikan. Buletin Ilmiah Gukuryoku I: 15-20.
Syamsuhidayat dan Hutapea. 1991. Inventaris Tanaman Obat Indonesia, 305-306, Departemen Kesehatan Republik Indonesia, Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan, Jakarta.
Ukhroy N U. 2008. Efektifitas Penggunaan Propolis Terhadap Nisbah Kelamin Ikan Guppy (Poecilia reticulata).
Zairin J R M. 2002. Sex Reversal: Memproduksi Benih Ikan Jantan atau Betina. Penebar Swadaya. Jakarta.
Zumrotun, Masyud B dan Thohari AM. 2006. Peranan sanrego Lunasia amara Blanco dalam peningkatan libido seksual rusa timur Cervus Timorensis de Blainville. Media Konservasi 11: 72–76.