In-Vivo Test Addition of Dunaliella salina Extract to Commercial Feed on Clinical Symptoms and Anatomical Pathology of Cantang Grouper after Viral Nervous Necrosis (VNN) infection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46252/jsai-fpik-unipa.2022.Vol.6.No.2.231Keywords:
VNN PathologyAbstract
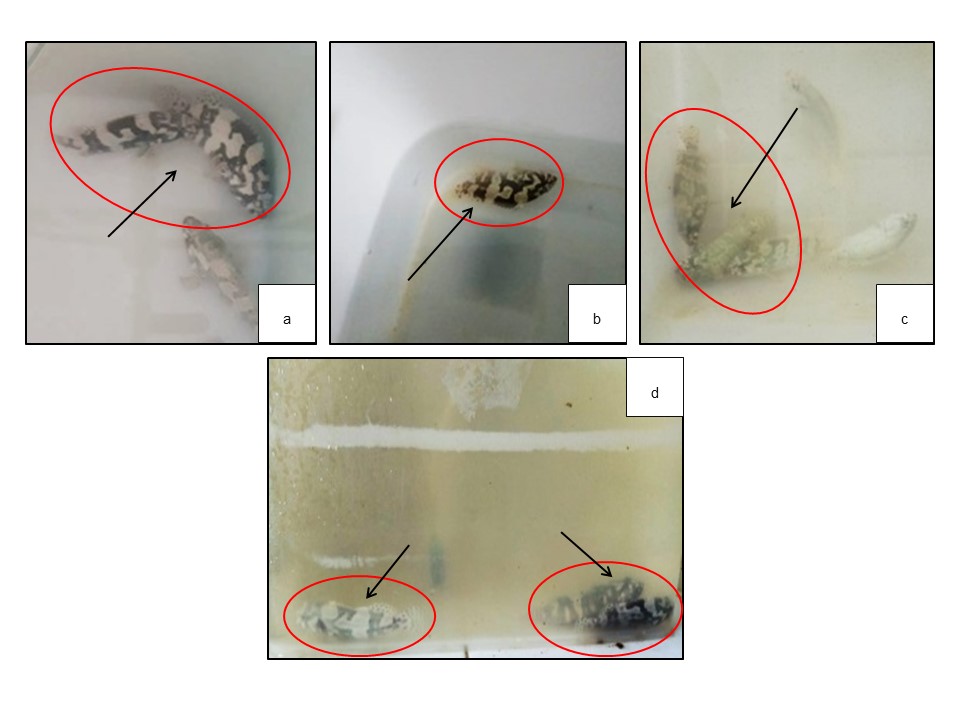
Viral Nervous Necrosis (VNN) is a pathogen that is often found infecting cantang grouper and causing mass mortality of up to 100% in a short time. VNN is caused by a Nodavirus infection that infects the nervous and visual systems of fish. One of the prevention efforts against VNN infection in cantang grouper is to add Dunaliella salina extract which contains -carotene, nephtalene, tetradecane and phenol which acts as antiviral, anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory. The purpose of this study was to examine the potency of D. salina extract against clinical symptoms and anatomical pathology of cantang grouper after VNN infection. D. salina extract with doses of 250, 300, 350 and 400mg/kg of feed was added to commercial pelleted feed of the Stella B2 brand with a protein content of 42%. Feed was given to cantang grouper measuring 7-9 cm for 10 days of maintenance. Furthermore, the fish were challenged using VNN as much as 0.2 ml/head through the injection method. Observations of clinical symptoms and anatomical pathology were observed for 96 hours after infection. Symptoms of clinical pathology of fish infected with VNN appear to be circling, swimming horizontally, inflation of the swim bladder, discoloration of the pectoral fins to reddish, swollen lymph organs, yellowing of the liver and darkening of the body color. The compounds found in the extract of D. salina can be used to increase the immune response and reduce the number of deaths of cantang grouper infected with VNN. The addition of D. salina extract which was higher than other doses could increase the immune system so that its survival (SR) was higher as the dose increased.
Downloads
References
Adipu, Y., Lumenta. C, Kaligis. E dan H. J. Sinjal. (2013). Kesesuaian lahan budidaya laut di perairan Kabupaten Bolaang Mongondow Selatan, Sulawesi Utara. Jurnal Perikanan dan Kelautan Tropis. 9 (1): 19-26.
Cakmak, Y. S., Kaya. M and M. Asan-Ozusaglam. (2014). Biochemical composition and bioactivity screening of various extracts from Dunaliella salina, a green microalga. EXCLI Journal. 13: 679-690.
Cepeda, G. N., B. B. Santoso, M. M. Lisangan dan I. Silamba. (2018). Kandungan fenol, flavonoid dan terpenoid ekstrak metanol daun akway (Drimys piperita Hook f.). Agrotek. 1: 35-40.
Chuang, W., Ho. Y, Liao. J and F. Lu. (2014). Dunaliella salina exhibits an antileukemic immunity in a mouse model of WEHI 3 leukemia cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 62 (47): 11479-11487.
Dai, J., Wu. Y, Chen. S, Zhu. S, Yin. H, Wang. M and J. Tang. (2010). Sugar compositional determination of polysaccharides from Dunaliella salina by modified RP-HPLC method of precolumn derivatization with 1-phenyl-2methyl-5-pyrazolone. Carbohydrate Polymers. 82 (3): 629-635.
Dedi, H. Irawan dan W. K. A. Putra. (2018). Pengaruh pemberian hormone tiroksin pada pakan pelet megami terhadap pertumbuhan benih ikan kerapu cantang Epinephellus fuscoguttatus-lanceolatus. Intek Akuakultur. 2 (2): 33-48.
Duan, W., F. Meng, Y. Lin and G. Wang. (2017). Toxicological effects of phenol on four marine microalgae. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 52: 170-176.
ajri, N. A., M. Ali dan S. N. Depamede. (2015). Deteksi WSSV (White Spote Syndrome Virus) pada lobster air tawar (Procambarus clarkii) menggunakan metode real-time PCR. Jurnla Sains Teksnologi dan Lingkungan. 1(1): 30-36.
Hadiyanto dan M. Azim. (2012). Mikroalga: Sumber Pangan dan Energi Masa Depan. Edisi Pertama. UPT UNDIP Press. Semarang. 138 hlm.
Hakim, M. A., Indriasih dan W. Wiyani. (2016). Penyakit Ikan Kerapu: Bab VII Penyakit Viral. LP2IL. Serang. 75 hlm.
Hexin, X. Cui, F. Wahid, F. Xia, C. Zhong and S. Jia. (2016). Analysis of the physiological and molecular responses of Dunaliella salina to macronutrient deprivation. Plos One. 11(3): 1-19.
Ibanez, E and A. Cifuentes. (2013). Benefit of using algae as natural source of functional ingredient. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 93 (4): 703-709.
InterClinical Laboratories. (2010). Dunaliella salina-Marine Phyto-plankton. Practitioner Informa-tion.
Johnny, F., Mahardika. K, Giri, I. N. A dan D. Roza. (2007). Penambahan vitamin c dalam pakan untuk meningkatkan imunitas benih ikan kerapu macan, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus terhadap infeksi Viral Nervous Necrosis. Jurnal Akuakultur Indonesia. 6 (1): 43 – 53.
Korsnes, K. (2008). Nervous Necrosis Virus (VNN) in farmed Norwegian fish species. Thesis of Philosopiae Doctor (PhD) University of Bergen. Norway: Bergen.
Lio-Po, G. D and L. D. de la Pena. (2004). Viral Diseases Chapter 1. Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center. Philippines. Hlm 3-18.
Luin, M., F. F. Ching and S. Senoo. (2013). Sexual maturation and gonad development in Tiger Grouper (Epinephelus Fuscoguttatus) X Giant Grouper (E. Lanceolatus) hybrid. J Aquac Res Development. 5(2): 1-5.
Madhumathi, M. and R. Rengasamy. (2011). Antioxidant status of Penaeus monodon fed with Dunaliella salina supplemented diet and resistance against WSSV. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology. 3(10): 7249-7159.
Mahardika, K. dan I. Mastuti. (2013). Studi histopatologi: pembentukan sel-sel membesar pada organ ikan kerapu setelah terinfeksi Megalocytivirus. Konferensi Akuakultur Indonesia. 132-138.
Nazari, A., M. D. Hassan, M. J. Zorriehzahra, T. I. Azmi and S. S. Arshad. (2014). Pathogenicity of viral nervous necrosis virus for guppy fish, Poecilia reticulata. Irian Journal of Fisheries Science. 13(1): 168-177.
Novriadi, R., S. Agustatik, S. Bahri, D. Sunantara dan E. Wijayanti. (2014). Distribusi patogen dan kualitas lingkungan pada budidaya perikanan laut di Provinsi Kepulauan Riau. Depik. 3(1): 83-90.
Roza, D., F. Johnny dan Tridjoko. (2006). Peningkatan respon imun non-spesifik benih Kerapu Bebek (Cromileptes altivelis) dengan imunostimulan dan bakterin terhadap infeksi Viral Nervous Necrosis (VNN). Jurnal Perikanan. 8(1): 25-35.
Priyadarshani, I. dan B. Rath. (2012). Commercial and industrial applications of micro algae- a review. J. Algal Biomass Utln. 3(4): 89-100.
Setyorini, N., Khusnah. A dan L. Widajatiningrum. (2008). Kelangsungan hidup ikan koi (Cyprinus carpio) yang terinveksi KHV (Koi Herpes Virus). Berkala Ilmiah Perikanan. 3 (1): 57-65.
Sudaryatma, P. E., A. T. Lestari, N. L. Sunarsih, K. S. Widiarti, S. N. Hidayah, D. Srinoto. (2012). Imunositokimia Streptavidin Biotin: deteksi dini Viral Nervous Necrosis Virus pada lendir ikan Kerapu Macan (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus). Jurnal Sain Veteriner. 30(1): 99-109.
Sumaryam., Kusyairi, Oetami. S, Suprapto. H dan G. C. de Vries. 2011. Kultur sel otak dan mata ikan kerapu (Chromileptes altivelis) untuk replikasi Viral Nervous Necrosis (VNN). Berita Biologi. 10 (4): 505-510.
Sutarmat, T dan H. T. Yudha. (2013). Analisis keragaan pertumbuhan benih kerapu hibrida hasil hibridisasi kerapu macan (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus) dengan kerapu kertang (Epinephelus lanceolatus) dan kerapu batik (Epinephelus microdon). J. Ris. Akuakultur. 8 (3): 363-372.
Tarsim., A. Setyawan, E. Harpen dan A. R. Pratiwi. (2013). The effication of Black Cummin (Nigella sativa) as immunostimulant in Humpback Grouper (Cromileptes altivelis) againts VNN (Viral Nervous Necrosis) infection. Seminar Nasional Sains dan Teknologi V Lembaga Penelitian Universitas Lampung. 525-532.
Udiarta, P., E. N. Dewi dan Romadhoni. (2015). Pengaruh pemberian MgCO3 dan ZnCl2 terhadap stabilitas kandungan pigmen klorofil pada mikroalga Spirulina platensis. Journal of Fisheries Science and Technology. 10(2): 114-118.
Woo, P. T. K. and R. C. Cipriano. (2017). Fish Viruses and Bacteria Pathobiology and Protection. CABI. UK. 364 p.
Yunanto, Y., H. P. Kusumaningrum dan S. Pujiyanto. (2013). Fusi protoplas interspesies Chlorella pyrenoidosa dan Dunaliella salina. Jurnal Sains dan Matematika. 21(1): 15-30.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Rani Yuwanita, Ating Yuniarti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


















